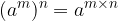The term 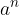 , where
, where 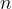 is a natural number, is the shorter notation for the product of
is a natural number, is the shorter notation for the product of 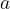 multiplied by
multiplied by 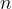 number of times. The number
number of times. The number 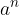 is also called
is also called 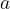 raised to the power of the number
raised to the power of the number 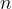 . The number
. The number 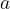 is called the base, and the number
is called the base, and the number 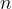 is called the degree, powers or exponent.
is called the degree, powers or exponent.
The term 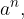 for which
for which 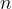 is a natural number is the shorter notation for the number of times
is a natural number is the shorter notation for the number of times 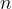 a given number
a given number 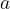 has to be multiplied.
has to be multiplied.
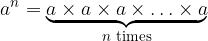
There are some properties of exponentiation.
The potency value 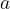
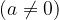 with a negative integer exponent is:
with a negative integer exponent is:
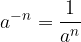
For 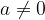 and
and 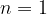 it is
it is
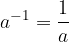
which is the inverse value of the number a.
The value of the power with any nonzero base and exponent 0 is 1:
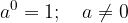
A summary of the rules for calculating with powers (the rules are explained in more detail below) is summarized in the following table:
Multiplication and division of powers by the same bases
The rule for multiplying powers by the same basis is determined by first writing both powers as the product of the same factors.
Potentials with the same bases are multiplied by overwriting the base and adding the power exponents:
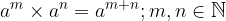
When dividing powers by the same bases, we act similarly as when multiplying.
Exponents with the same bases are divided by writing down the base and subtracting the exponents:
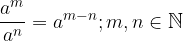
Multiplication and division of powers by equal exponents
The rule for multiplying powers by the same exponents is determined by first writing both powers as the product of the same factors, then multiplying the different factors and writing the result by the power.
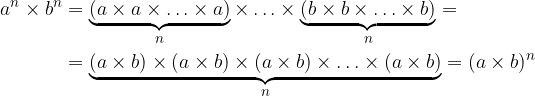
Terms with the same exponents and different bases are multiplied by multiplying the bases and overwriting the exponent:
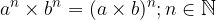
When dividing powers by the same exponents, we act similarly to multiplication.
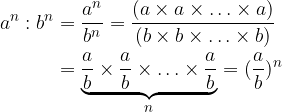
Terms with the same exponents and different bases are divided by dividing the bases and overwriting the exponent:
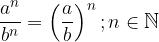
Exponents of exponentials are gotten by overwriting the base and multiplying the potential exponents: