Personal collections


A number in index form consists of a base and an exponent (power).
A number with an exponent 0 is also called the zero power. Its result is always equal to 1.
Zero power:
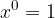
The number with exponent 1 is the base itself.
A number with exponent 1:
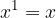
A number with a negative base and an even exponent is a positive number:
A number with a negative base and an even exponent:
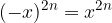
The number with a negative base and an odd exponent is a negative number:
A number with a negative base and an odd exponent:
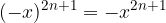
When products have a common power, we evaluate the powers separately.
Powers of products:
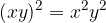
When quotients have a common power, we evaluate the powers separately.
Powers of quotients:
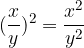
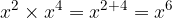
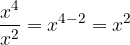
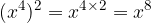
We can only add powers over the same base and exponent, namely, we add the coefficients and overwrite the base and exponent.
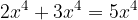
We can only subtract powers with the same base and exponent, namely, subtract the coefficients and overwrite the base and exponent.
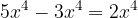
When adding or subtracting the powers with the same base and different exponent, we can highlight the common factor by writing the base to the smallest exponent before the parenthesis, and the remaining terms reduced by the exposed exponent are written in parenthesis.