Personal collections


State the basic assumption of the kinetic theory of gases that leads to the conclusion that there is zero potential energy between the molecules of an ideal gas.
The pressure 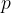 and volume
and volume 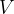 of an ideal gas are related by
of an ideal gas are related by
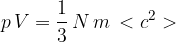
where 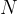 is the number of molecules,
is the number of molecules, 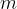 is the mass of a molecule and
is the mass of a molecule and 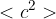 is the mean square speed of the molecules. Use this equation to show that the mean kinetic energy
is the mean square speed of the molecules. Use this equation to show that the mean kinetic energy 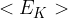 of a molecule is given by
of a molecule is given by
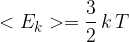
where 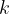 is the Boltzmann constant and
is the Boltzmann constant and 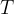 is the thermodynamic temperature.
is the thermodynamic temperature.
A cylinder contains 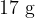 of oxygen gas at a temperature of
of oxygen gas at a temperature of 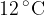 . The mass of
. The mass of 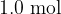 of oxygen gas is
of oxygen gas is 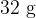 . It may be assumed that the oxygen behaves as an ideal gas. Calculate, for the oxygen gas in the cylinder,
. It may be assumed that the oxygen behaves as an ideal gas. Calculate, for the oxygen gas in the cylinder,
the mean kinetic energy of a molecule,
the number of molecules.