Personal collections


Define magnetic flux density.
An insulated rectangular coil of wire, consisting of 40 turns, is suspended in a cradle from a newton meter, as shown in the figure below.
The vertical sides of the coil have a length of 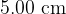 and the horizontal sides have a length of
and the horizontal sides have a length of 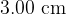 . The initial reading on the newton meter is
. The initial reading on the newton meter is 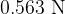 . A U-shaped magnet rests on a top-pan balance that is set to a reading of
. A U-shaped magnet rests on a top-pan balance that is set to a reading of 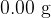 . The lower edge of the coil is lowered into the region between the poles of the U-shaped magnet, as shown in the side view in the figure below.
. The lower edge of the coil is lowered into the region between the poles of the U-shaped magnet, as shown in the side view in the figure below.
The magnetic field in the region between the poles is uniform. The lower edge of the coil is entirely within the uniform magnetic field. A current of 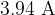 is now passed through the coil. This causes the reading on the top-pan balance to change to
is now passed through the coil. This causes the reading on the top-pan balance to change to 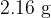 .
.
Explain why the current causes a vertical force to act on the coil.
Determine, to three significant figures, the flux density B of the uniform magnetic field.
Determine what is now the reading on the newton meter. Explain your reasoning.