Personal collections


An electron is travelling in a vacuum at a speed of 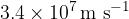 . The electron enters a region of uniform magnetic field of flux density
. The electron enters a region of uniform magnetic field of flux density 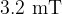 , as illustrated in the figure below.
, as illustrated in the figure below.
The initial direction of the electron is at an angle of 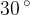 to the direction of the magnetic field.
to the direction of the magnetic field.
When the electron enters the magnetic field, the component of its velocity 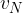 normal to the direction of the magnetic field causes the electron to begin to follow a circular path. Calculate:
normal to the direction of the magnetic field causes the electron to begin to follow a circular path. Calculate:
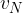
the radius of this circular path.
State the magnitude of the force, if any, on the electron in the magnetic field due to the component of its velocity along the direction of the field.
Use information from (a) and (b) to describe the resultant path of the electron in the magnetic field.