Personal collections


A prism is an angular geometric body bounded by two congruent and parallel n - angles (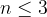 ) and n parallelograms.
) and n parallelograms.
The base surface of the prism is represented by equal and parallel n - angles.
The side faces of the prism are formed by parallelograms.
Base length are the sides that make the base area.
All other sides are called side lengths and are parallel and of equal length.
Prism height is the distance between the base surfaces.
The prism is named after the n - angle in the base surface, so prism can be three-sided, four-sided, five-sided ...
We know vertical, oblique, regular and uniform prisms.
Prisms are divided into vertical and oblique prisms.
Vertical prisms are prisms that have a side perpendicular to the base surface. The length of the side is equal to the height of the prism.
In the case of oblique prisms, the side are not perpendicular to the base surface and are longer than the height of the prism.
Regular prism is a vertical prism that has a regular n - angle (equilateral triangle, square, ...) as the base surface
Equilateral prism is a prism that has all sides of equal length.
The surface area of a prism is the sum of the areas of all its surfaces. Label it with the letter A.
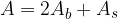
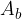 - base surface area
- base surface area
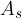 - the area of the body surfaces which is equal to the sum of the areas of all side surfaces
- the area of the body surfaces which is equal to the sum of the areas of all side surfaces
The volume of a prism is the size of the space that the prism occupies. Label it with the letter V.
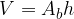
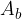 - base surface area
- base surface area
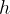 - prism height
- prism height