

A dodecahedron is a regular polyhedron bounded by 12 regular pentagons. On each face, write one of the numbers from 1 to 12, which are not repeated.
We roll two numbered dodecahedra at the same time. What is the probability of the event A that the sum of the numbers on the two upper faces is a prime number, less than or equal to 5?
One numbered dodecahedron is rolled 20 times. What is the probability of the event B that in these 20 repetitions of the experiment, the number 7 will appear on the top face exactly 3 times? Round the result to three decimal places.
Make the edge length of the dodecahedron equal to 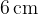 . Calculate the sum of the lengths of all the edges and the area of this dodecahedron.
. Calculate the sum of the lengths of all the edges and the area of this dodecahedron.