Personal collections


A pyramid is a polyhedron formed by joining the vertices of a polygon that forms the base with the apex where all the triangle-shaped lateral faces meet. A pyramid with a base with n sides contains (n+1) number of vertices and 2n edges.
Base: The flat face in which the pyramid rests.
The lateral faces: The triangular faces connecting the base a the apex.
Vertices: The corners:
Edges: Where any two faces meet.
Height: The perpendicular distance between the base surface and the top of the pyramid.
Slant height: The imaginary line drawn from the mid-point of any base edge to the apex.
A pyramid is named after the polygon at the base of the pyramid, so a pyramid can be three-sided, four-sided, five-sided and so on.
Right and oblique pyramids:
We divide pyramids into right and oblique pyramids.
Right pyramids are pyramids whose apex is exactly over the middle of its base. The perpendicular line from the apex to the base centre is the height.
Oblique pyramids are pyramids whose apex is not exactly over the middle of its base. The perpendicular line from the apex to the base is the height.
A regular pyramid is a pyramid that has equal sides and angle (equilateral triangle, square, ...) as its base.
Irregular Pyramid is such a pyramid whose base is an irregular polygon (sides not equal to each other). Its lateral faces are different.
The area of a pyramid is the sum of the areas of all its boundary surfaces. Denoted by SA.
Surface area of a pyramid:
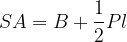
where,
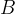 - base area
- base area
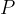 - base perimeter
- base perimeter
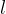 - slant height
- slant height
The volume of a pyramid is the size of the space that the pyramid occupies. Denoted by V.
Volume of a pyramid:
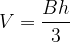
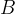 - base area
- base area
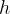 - height of the pyramid
- height of the pyramid