Personal collections


A quadratic inequality can have the following forms:
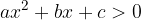
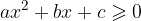
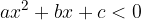
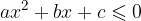
The solutions of a quadratic inequality are obtained by finding where the corresponding quadratic function 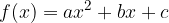 is positive, negative or equal to zero.
is positive, negative or equal to zero.
The function 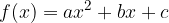 has the form:
has the form:
The function 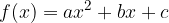 has the form:
has the form:
The function 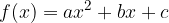 has the form:
has the form:
The 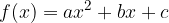 function has the form:
function has the form:
The function 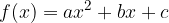 takes the form:
takes the form:
The function 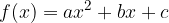 takes the form:
takes the form: