Personal collections


State what is meant by radioactive decay.
An unstable nuclide P has decay constant 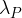 and decays to form a nuclide D. This nuclide D is unstable and decays with decay constant
and decays to form a nuclide D. This nuclide D is unstable and decays with decay constant 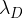 to form a stable nuclide S. The decay chain is illustrated in the figure below.
to form a stable nuclide S. The decay chain is illustrated in the figure below.
The symbols P, D and S are not the nuclide symbols. Initially, a radioactive sample contains only nuclide P. The variation with time 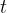 of the number of nuclei of each of the three nuclides in the sample is shown in the graph below.
of the number of nuclei of each of the three nuclides in the sample is shown in the graph below.
On the graph above, use the symbols P, D, and S to identify the curve for each of the three nuclides.
The half-life of nuclide P is 60.0 minutes. Calculate the decay constant 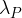 , in
, in 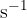 , of this nuclide.
, of this nuclide.
In the decay chain shown in the figure above, 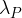 is approximately equal to
is approximately equal to 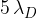 . The decay chain of a different nuclide E is illustrated in the figure below.
. The decay chain of a different nuclide E is illustrated in the figure below.
The decay constant 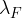 of nuclide F is very much larger than the decay constant
of nuclide F is very much larger than the decay constant 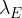 of nuclide E. By reference to the half-life of nuclide F, explain why the number of nuclei of nuclide F in the sample is always small.
of nuclide E. By reference to the half-life of nuclide F, explain why the number of nuclei of nuclide F in the sample is always small.