Personal collections


A linear inequality is a relationship that hold between two different components. The components are the left hand side and the right hand side of the inequality. And they are connected with any of the following signs:
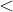 , which means less than
, which means less than
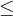 which means less than or equal to
which means less than or equal to
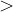 , which means greater than
, which means greater than
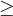 which means greater than or equal to
which means greater than or equal to
Variables also appear in inequality, which in this case are called unknowns. Most often, the unknown is marked with the letter x.
In general, a linear inequality is of the following form:
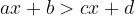
where a, b, c, d are real numbers.
When solving inequalities, we use the following procedures, which are due to the properties of the order relation of real numbers:
to the left and right sides of the inequality we can add the same number (or unknown or longer mathematical expression)
the left and right sides of the inequality can be multiplied or divided by the same positive number (or unknown or longer mathematical expression)
the left and right sides of the inequality can be multiplied or divided by the same negative number, but in this case, the inequality is reversed
A linear inequality with one unknown is solved by transferring the terms with the unknown to one side and the terms without the unknown to the other side.
Exactly one of the following statements applies to the solution of a linear inequality with one unknown:
The solution to the inequality is a real number to which the inequality applies - so if we insert this number instead of the unknown, we get the correct notation. The set of solutions of a linear inequality is an interval that is not limited to at least one value.