Personal collections


An ideal gas has a volume of 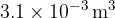 at a pressure of
at a pressure of 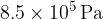 and a temperature of
and a temperature of 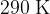 , as shown in the figure below.
, as shown in the figure below.
The gas suddenly expands to a volume of 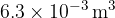 . During the expansion, no thermal energy is transferred. The final pressure of the gas is
. During the expansion, no thermal energy is transferred. The final pressure of the gas is 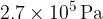 at temperature
at temperature 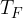 , as shown in the figure above.
, as shown in the figure above.
Show that the number of gas molecules is 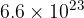 .
.
Show that the final temperature 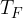 of the gas is
of the gas is 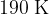 .
.
The average translational kinetic energy 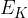 of a molecule of an ideal gas is given by
of a molecule of an ideal gas is given by
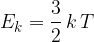
where 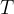 is the thermodynamic temperature and
is the thermodynamic temperature and 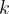 is the Boltzmann constant. Calculate the increase in internal energy
is the Boltzmann constant. Calculate the increase in internal energy 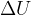 of the gas.
of the gas.
Use the first law of thermodynamics to explain why the external work 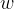 done on the gas during the expansion is equal to the increase in internal energy in (b)(ii).
done on the gas during the expansion is equal to the increase in internal energy in (b)(ii).